How Backward Integration Management Software Drives Efficiency and Sustainability
Backward integration management software refers to digital solutions that enable businesses to manage the operations of their upstream supply chains effectively.
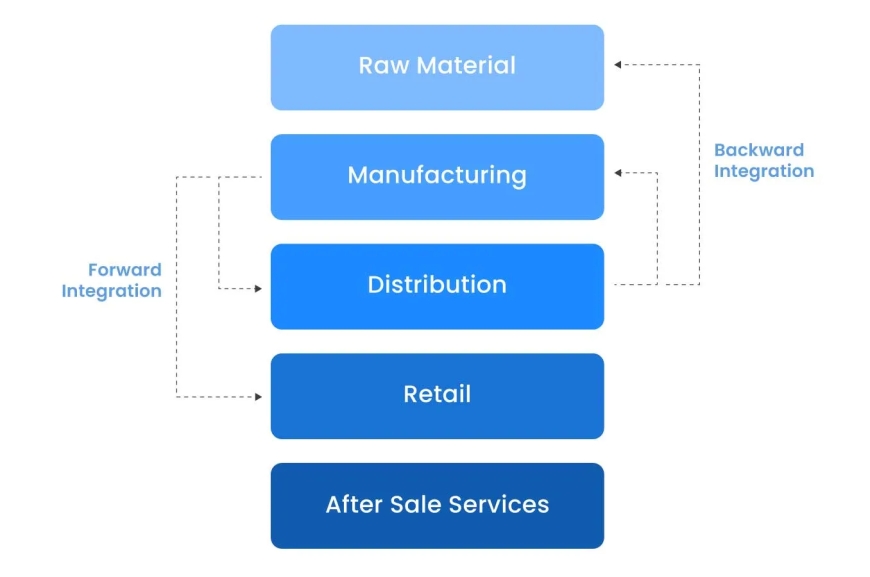
In todays competitive agricultural landscape, companies are incorporating backward integration management software to automate operations, cut costs, and promote sustainability. The cutting-edge technology enables organisations to manage and control their supply chains effectively, right from procuring raw materials to providing finished goods. Further, unifying sustainability with backward integration has become a foundation for promoting responsible growth within the sector.
What is backward integration management software?
Backward integration management software refers to digital solutions that enable businesses to manage the operations of their upstream supply chains effectively. This includes:
Businesses can either source raw materials directly from suppliers or take ownership of the supply chain.
Managing production inputs, logistics, and quality control through centralised platforms.
Enhancing transparency and accountability across every stage of the supply chain.
These software solutions are designed to simplify complex processes, reduce dependency on third-party vendors, and ensure that resources are allocated optimally.
The Role of Backward Integration in Sustainability
Incorporating sustainability with backward integration helps businesses meet environmental and social goals while maintaining profitability. By having greater control over their supply chains, companies can adopt eco-friendly practices, such as:
1. Reducing Waste:
Streamlined operations minimise raw material wastage, promoting efficient resource use.
2. Adopting Green Inputs:
Businesses can prioritise sustainable suppliers who provide organic or eco-friendly inputs.
3. Improving Traceability:
Backward integration ensures every products journey is traceable, meeting consumer demand for transparency.
4. Lowering Carbon Footprint:
Efficient logistics planning through software reduces emissions associated with transportation.
Key Features of Backward Integration Management Software
1. Inventory Management:
Monitor and manage stock levels to avoid shortages or overproduction.
2. Real-Time Analytics:
Access insights into supply chain performance and identify areas for improvement.
3. Supplier Collaboration:
Build strong relationships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery and quality assurance.
4. Compliance Tracking:
Ensure adherence to environmental and industry regulations seamlessly.
By integrating these features, businesses not only optimise their operations but also align with global sustainability goals.
Benefits of Using Backward Integration Management Software
Enhanced Efficiency: Automates manual processes, saving time and resources.
Cost Savings: Reduces reliance on intermediaries and streamlines procurement.
Better Quality Control: Enables businesses to monitor and maintain product standards.
Competitive Advantage: Companies can offer better prices and quality, gaining an edge in the market.
Also Read - The Role of Backward Integration in Agriculture for Sustainable Growth
Challenges and Solutions
While the adoption of backward integration and associated software presents numerous benefits, some challenges include:
High Initial Costs: Investment in advanced software can be expensive.
Training Requirements: Employees need proper training to use the software effectively.
These challenges can be addressed through phased implementation and partnerships with technology providers offering cost-effective solutions.
Conclusion
Backward integration management software is revolutionising supply chain management by improving efficiency and promoting sustainability. By integrating advanced features and aligning with eco-friendly practices, businesses can harness the power of backward integration to achieve long-term success. Emphasising sustainability with backward integration ensures that growth is both responsible and profitable, paving the way for a resilient agricultural future.




























